Acid-Base Regulation and Body Temperature Developments in Critical Care: A Comprehensive Guide

Acid-base regulation and body temperature are vital physiological parameters in critical care. Alterations in either can have profound effects on cellular function, organ dysfunction, and patient outcomes. Understanding the mechanisms and consequences of acid-base disturbances and temperature abnormalities, as well as their interplay, is essential for optimal patient management.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6979 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 262 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
This comprehensive guide will explore the latest developments in acid-base regulation and body temperature management in critical care. We will delve into the fundamental principles of pH regulation, temperature homeostasis, monitoring techniques, and clinical strategies to address acid-base imbalances and temperature abnormalities.
Acid-Base Regulation
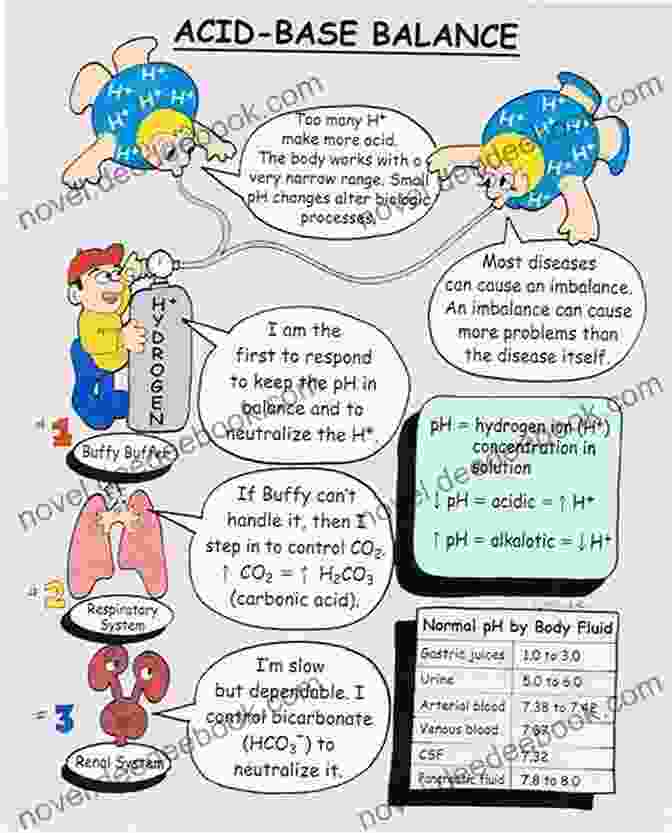
Acid-base regulation refers to the body's ability to maintain the pH of its extracellular fluid (ECF) within a narrow range, typically between 7.35 and 7.45. pH is a measure of acidity or alkalinity, with lower pH values indicating acidity and higher pH values indicating alkalinity.
The body has several mechanisms to regulate pH, including:
- Respiratory regulation: The lungs regulate pH by adjusting the rate and depth of breathing, which affects the amount of carbon dioxide (CO2) in the blood. CO2 is an acid, so increased ventilation lowers CO2 levels and raises pH (respiratory alkalosis). Conversely, decreased ventilation increases CO2 levels and lowers pH (respiratory acidosis).
- Renal regulation: The kidneys regulate pH by adjusting the excretion of hydrogen ions (H+) and bicarbonate ions (HCO3-). Increased H+ excretion lowers pH (metabolic acidosis),while increased HCO3- excretion raises pH (metabolic alkalosis).
- Buffer systems: Buffers are chemical substances that can absorb or release H+ ions, thereby minimizing changes in pH. The most important buffer in the ECF is bicarbonate, which can combine with H+ to form carbonic acid (H2CO3).
Acid-base disturbances occur when one or more of these regulatory mechanisms is impaired, leading to a change in ECF pH. Acid-base disturbances are classified as either metabolic or respiratory, depending on the underlying cause.
Body Temperature Regulation
Body temperature regulation refers to the body's ability to maintain a constant core temperature, typically around 37°C (98.6°F). Temperature regulation is critical for optimal organ function and cellular metabolism.
Body temperature is regulated by a complex interplay of several mechanisms, including:
- Hypothalamus: The hypothalamus, a part of the brain, acts as the body's thermostat, comparing the current core temperature to a set point and initiating appropriate responses.
- Thermoregulation centers: Thermoregulation centers in the hypothalamus and spinal cord control heat production and dissipation by activating or inhibiting effectors such as blood vessels, sweat glands, and muscles.
- Thermoreceptors: Thermoreceptors in the skin, internal organs, and brain monitor temperature changes and transmit this information to the hypothalamus.
In response to temperature changes, the body has several mechanisms to maintain core temperature, including:
- Vasoconstriction: When body temperature drops, blood vessels in the skin constrict, reducing blood flow to the skin's surface and conserving heat.
- Vasodilation: When body temperature rises, blood vessels in the skin dilate, increasing blood flow to the skin's surface and promoting heat dissipation through radiation and evaporation.
- Shivering: Shivering is a involuntary muscle contraction that generates heat, typically in response to cold exposure.
- Sweating: Sweating is a process that releases heat through the evaporation of water from the skin.
Temperature abnormalities occur when the body's thermoregulation mechanisms are unable to maintain core temperature within a narrow range. Hypothermia is a body temperature below 35°C (95°F),while hyperthermia is a body temperature above 40°C (104°F).
Interplay between Acid-Base Regulation and Body Temperature
Acid-base regulation and body temperature are closely linked. Alterations in one can have a significant impact on the other.
- Hypothermia: Hypothermia causes a shift in the oxygen dissociation curve, reducing the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen. This can lead to tissue hypoxia and metabolic acidosis.
- Hyperthermia: Hyperthermia increases cellular metabolism, resulting in increased production of CO2 and metabolic acidosis.
- Metabolic acidosis: Metabolic acidosis stimulates ventilation, leading to respiratory alkalosis.
- Respiratory acidosis: Respiratory acidosis can lead to hypothermia as a result of reduced metabolic activity.
Understanding the interplay between acid-base regulation and body temperature is essential for the effective management of critically ill patients.
Monitoring Acid-Base and Body Temperature in Critical Care
Continuous monitoring of acid-base status and body temperature is crucial in critical care to detect and manage abnormalities promptly.
Acid-base monitoring: Acid-base status is typically assessed through arterial blood gas analysis, which measures pH, PaCO2, HCO3-, and lactate. Lactate is a marker of anaerobic metabolism and can indicate tissue hypoxia and metabolic acidosis.
Temperature monitoring: Body temperature is typically monitored using rectal, axillary, or esophageal probes. Core temperature is considered the most reliable measure of body temperature.
Continuous monitoring allows healthcare professionals to track changes in acid-base status and body temperature over time and intervene as needed.
Clinical Management
The management of acid-base disturbances and temperature abnormalities in critical care involves a multidisciplinary approach, including:
Acid-base management: Treatment of acid-base disturbances depends on the underlying cause and the severity of the imbalance. It may involve administering fluids, electrolytes, or medications to correct pH and improve oxygen delivery.
Temperature management: Hypothermia and hyperthermia require specific management strategies, including warming measures (e.g., blankets, warming devices) and cooling measures (e.g., cooling blankets, ice packs) respectively.
In severe cases, mechanical ventilation, renal replacement therapy, or extracorporeal membrane oxygenation (ECMO) may be necessary to support organ function and maintain acid-base balance.
Recent Developments and Advances
Continuous research and technological advancements are shaping the field of acid-base regulation and body temperature management in critical care.
- Non-invasive monitoring: Non-invasive monitoring techniques, such as transcutaneous pH and temperature sensors, offer less invasive alternatives to traditional arterial blood gas analysis and rectal probes.
- Personalized thermoregulation: Advances in thermoregulation monitoring and control systems allow for personalized temperature management, optimizing outcomes in critically ill patients with varying thermoregulatory needs.
- Novel therapeutics: Research is ongoing to develop new medications and therapies to target acid-base disturbances and temperature abnormalities more effectively.
These advancements have the potential to improve patient outcomes and reduce complications associated with acid-base imbalances and temperature abnormalities in critical care.
Acid-base regulation and body temperature are vital physiological parameters in critical care. Understanding the mechanisms, consequences, and interplay of acid-base disturbances and temperature abnormalities is essential for optimal patient management.
Continuous monitoring, prompt intervention, and a multidisciplinary approach are crucial for effective management of these conditions. Continuous research and technological advancements continue to refine our understanding and treatment strategies, improving outcomes for critically ill patients.
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6979 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 262 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |
Do you want to contribute by writing guest posts on this blog?
Please contact us and send us a resume of previous articles that you have written.
 Novel
Novel Page
Page Chapter
Chapter Text
Text Story
Story Genre
Genre Magazine
Magazine Newspaper
Newspaper Bookmark
Bookmark Shelf
Shelf Glossary
Glossary Foreword
Foreword Preface
Preface Synopsis
Synopsis Annotation
Annotation Footnote
Footnote Manuscript
Manuscript Codex
Codex Library card
Library card Biography
Biography Memoir
Memoir Narrator
Narrator Character
Character Resolution
Resolution Librarian
Librarian Borrowing
Borrowing Study
Study Academic
Academic Journals
Journals Reading Room
Reading Room Rare Books
Rare Books Special Collections
Special Collections Interlibrary
Interlibrary Study Group
Study Group Thesis
Thesis Dissertation
Dissertation Storytelling
Storytelling Reading List
Reading List Book Club
Book Club Textbooks
Textbooks Dewey Lambdin
Dewey Lambdin Kayla Perrin
Kayla Perrin Tom Means
Tom Means Hilary Moore
Hilary Moore Tiffany Lethabo King
Tiffany Lethabo King Jennifer Rudolph Walsh
Jennifer Rudolph Walsh Barbara Early
Barbara Early John Trenchard
John Trenchard Kenneth F Collier
Kenneth F Collier Denise Giles
Denise Giles Jason D Hill
Jason D Hill Jessica Flounder
Jessica Flounder Huping Ling
Huping Ling David Brock
David Brock John Mole
John Mole R H S Stolfi
R H S Stolfi Leo Black
Leo Black Matthew Dobbins
Matthew Dobbins Janet G Covey
Janet G Covey Jack Wilkinson
Jack Wilkinson
Light bulbAdvertise smarter! Our strategic ad space ensures maximum exposure. Reserve your spot today!

 Chance FosterThe Comprehensive Guide to the Reverse Diabetes Diet Plan: Restoring Health...
Chance FosterThe Comprehensive Guide to the Reverse Diabetes Diet Plan: Restoring Health... John GreenFollow ·18.1k
John GreenFollow ·18.1k Devin CoxFollow ·4k
Devin CoxFollow ·4k Pat MitchellFollow ·7.4k
Pat MitchellFollow ·7.4k Haruki MurakamiFollow ·9.9k
Haruki MurakamiFollow ·9.9k Bret MitchellFollow ·11.5k
Bret MitchellFollow ·11.5k Jerry HayesFollow ·4.6k
Jerry HayesFollow ·4.6k Leon FosterFollow ·14.1k
Leon FosterFollow ·14.1k Derrick HughesFollow ·9.1k
Derrick HughesFollow ·9.1k

 Bryce Foster
Bryce FosterPerforming Asian American Women On Screen And Scene
The representation of Asian American women...

 Frank Mitchell
Frank MitchellGirl Can Draw: A Spirited and Inspiring Play by Joe...
Prologue In the realm of...

 Marc Foster
Marc FosterThe Epic Story of Race and the American Media: A Journey...
From the Shadows of Slavery to the Dawn of...

 Demetrius Carter
Demetrius CarterThe Ultimate Guide to Hiking West Virginia: Discover the...
West Virginia, often referred to as...

 Isaiah Price
Isaiah PriceThe Ten Step Guide on How to Become Famous: Unleash Your...
In the captivating world of entertainment...
5 out of 5
| Language | : | English |
| File size | : | 6979 KB |
| Text-to-Speech | : | Enabled |
| Enhanced typesetting | : | Enabled |
| Print length | : | 262 pages |
| Screen Reader | : | Supported |